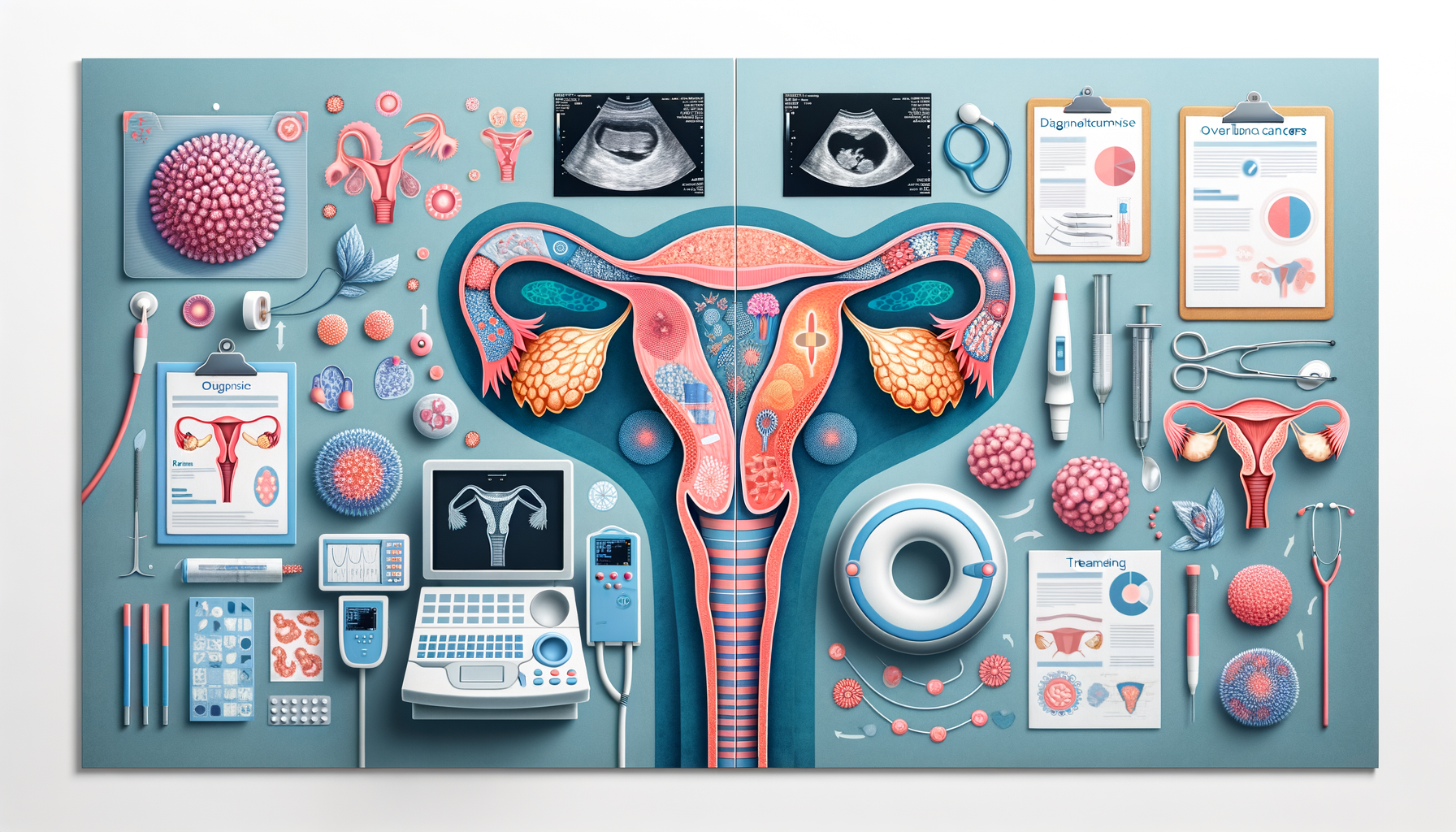
Top 4 Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer in Women
Ovarian cancer, often termed the “silent killer,” can be challenging to detect in its early stages because its symptoms are often subtle and easily mistaken for other common conditions. However, being aware of the signs can lead to earlier detection and better outcomes. Here are the top four symptoms to watch for:
1. Abdominal Bloating: Persistent bloating that doesn’t go away can be an early sign of ovarian cancer. This bloating is not the occasional discomfort that comes with a large meal but rather a constant feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen.
2. Pelvic or Abdominal Pain: Women may experience persistent pain or pressure in the pelvic region or abdomen. This discomfort is often different from menstrual cramps and should be discussed with a healthcare provider if it persists.
3. Difficulty Eating or Feeling Full Quickly: A sudden loss of appetite or feeling full after eating only a small amount can be indicative of ovarian cancer. This symptom often accompanies bloating and abdominal discomfort.
4. Urinary Symptoms: An increased need to urinate or urgent urination that is not related to a urinary tract infection can be a symptom. This change in urinary habits is often overlooked but should be monitored.
These symptoms can be caused by conditions other than ovarian cancer, but if they are new, persistent, and unusual for you, it is important to see a doctor for further evaluation.
How Ovarian Cancer is Diagnosed and Staged
Diagnosing ovarian cancer typically begins with a physical examination, including a pelvic exam. If cancer is suspected, several tests and procedures may be employed to confirm the diagnosis. These include:
- Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the ovaries and can help identify abnormal growths.
- CT Scans and MRIs: These provide detailed images of the body and can help determine the extent of the cancer.
- Blood Tests: The CA-125 blood test measures a protein that is often higher in women with ovarian cancer.
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue is removed and examined for cancer cells. This is often done during surgery.
Once diagnosed, the cancer is staged to determine its extent and spread. Staging is crucial for deciding the treatment plan and involves determining:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the ovaries.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby pelvic organs.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to the abdomen.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs.
Accurate staging helps in predicting the prognosis and tailoring the treatment approach.
Treatment Options Based on Cancer Type and Progression
The treatment of ovarian cancer depends on several factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, and the patient’s overall health. Here are the primary treatment options:
Surgery: Surgery is often the first line of treatment for ovarian cancer. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This may involve removing one or both ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, and nearby lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy: This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells and is often used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancerous cells. It can also be used as a primary treatment if surgery is not an option.
Targeted Therapy: This newer form of treatment focuses on the specific genetic changes in cancer cells. It can be effective in treating certain types of ovarian cancer with specific genetic markers.
Radiation Therapy: Although not commonly used for ovarian cancer, radiation can be employed to target specific areas where cancer has spread.
Each treatment plan is personalized, and a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers will work with the patient to determine the best course of action. Clinical trials may also be an option for some patients, offering access to new therapies.
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Proactive
Ovarian cancer is a complex disease, but understanding its symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options can empower women to take charge of their health. Early detection is key, and being aware of the signs can lead to timely medical intervention. Regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers are essential in managing health risks.
For those diagnosed with ovarian cancer, a tailored treatment plan offers the best chance for a positive outcome. Advances in medical research continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for many women affected by this disease. Staying informed and proactive is the best strategy in the fight against ovarian cancer.


Leave a Reply