Understanding Osteoarthritis of the Knee
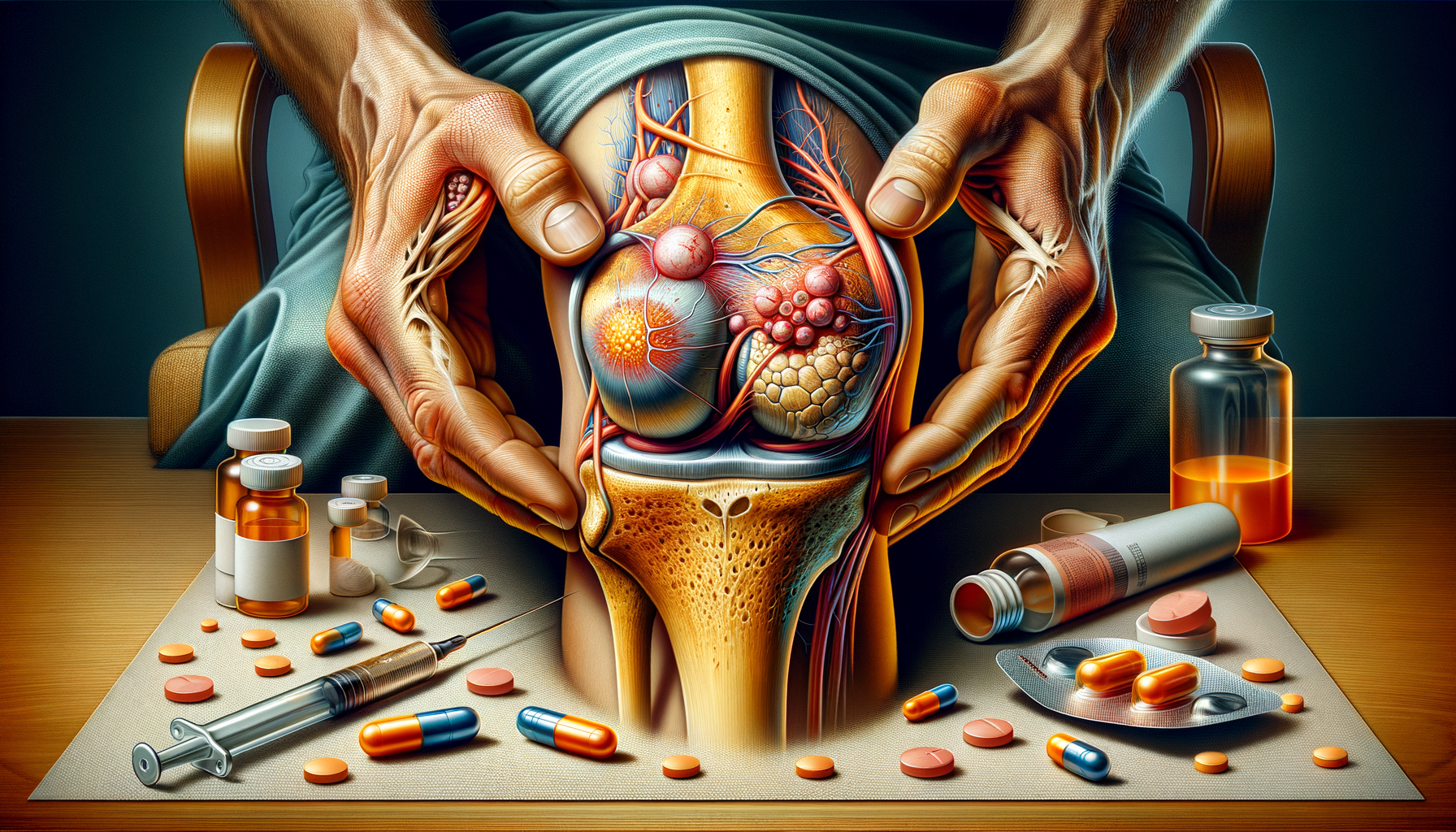
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions worldwide, becoming more prevalent with age. It is characterized by the gradual deterioration of cartilage, the protective tissue at the ends of bones, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Unlike other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis is primarily a wear-and-tear condition. The knee, being a weight-bearing joint, is particularly susceptible to this condition.
Several factors contribute to the development of knee osteoarthritis. Age is a significant factor, as the likelihood increases with advancing years. However, it is not merely an ailment of the elderly. Younger individuals can be affected, particularly if they have had knee injuries or surgeries. Obesity also plays a critical role, as excess weight increases the stress on knee joints, accelerating the wear of cartilage.
Understanding the mechanics of the knee can offer insight into why it is so vulnerable. The knee is a complex joint, involving bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons working in harmony. When this harmony is disrupted, whether by injury or degeneration, osteoarthritis can set in. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis early can lead to more effective management and a better quality of life. The symptoms often develop gradually and may vary in intensity. Initially, one might experience mild discomfort or stiffness, particularly after periods of inactivity or upon waking in the morning.
As the condition progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced. Pain during or after movement is common, and the knee may feel tender when pressure is applied. Swelling can occur due to inflammation in the joint, and the knee might feel warm to the touch. A grating sensation, often described as a “creaking” or “crunching” sound, can be heard during movement, indicating cartilage wear.
In advanced stages, the range of motion can be significantly reduced, making it challenging to perform daily activities. Walking, climbing stairs, or even standing for extended periods can become painful endeavors. In some cases, the knee may become unstable, leading to a sense of giving way or buckling.
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking medical advice is essential. Early intervention can slow the progression of the disease and improve one’s ability to manage symptoms effectively.
Exploring Treatment Options
Treating knee osteoarthritis involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on alleviating symptoms and improving joint function. While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, various treatments can help manage the condition effectively. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s lifestyle and health status.
Non-pharmacological treatments are often the first line of defense. Physical therapy can be beneficial, as exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the knee can enhance support and reduce stress on the joint. Weight management is another critical component, as reducing body weight can significantly decrease the load on the knees, alleviating pain and slowing cartilage deterioration.
Pharmacological treatments include pain relief medications such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide temporary relief.
For individuals with advanced osteoarthritis, surgical options might be considered. These can range from arthroscopic procedures to clean the joint, to partial or total knee replacement surgeries. Each treatment option comes with its benefits and risks, and decisions should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Innovative Approaches and Lifestyle Adjustments
In recent years, innovative approaches to managing knee osteoarthritis have emerged, offering new hope to those affected. One such approach is the use of hyaluronic acid injections, which aim to lubricate the joint and improve mobility. Although not suitable for everyone, this treatment can be effective for some individuals in reducing pain and enhancing joint function.
Another promising area of research is regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy. While still in the experimental stages, these treatments focus on repairing damaged cartilage and have shown potential in early studies. However, more research is needed to determine their long-term efficacy and safety.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis. Regular, low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling can help maintain joint flexibility and strengthen muscles without putting excessive strain on the knees. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can also support joint health.
Using supportive devices, such as knee braces or orthotic inserts, can provide additional stability and reduce pain during movement. Mind-body practices like yoga and tai chi can improve balance and flexibility, contributing to overall well-being.
Conclusion: Embracing a Proactive Approach
Managing knee osteoarthritis requires a proactive and informed approach. By understanding the nature of the condition, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring a range of treatment options, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life. While osteoarthritis is a chronic condition, advancements in medical treatments and lifestyle strategies offer hope for effective management.
Embracing a holistic approach that combines medical interventions with lifestyle adjustments can empower individuals to take control of their health. Regular communication with healthcare providers and staying informed about new developments in osteoarthritis research are vital components of a successful management plan.
Ultimately, the journey with knee osteoarthritis is unique to each individual. With the right tools and support, it is possible to navigate this condition with resilience and optimism.



Leave a Reply